As a small business owner, navigating the complex world of taxes can be overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. By implementing smart tax strategies, you can minimize your liability and maximize your savings. Tax savvy is not just about compliance; it’s about optimizing your financial performance. In this article, we’ll explore practical tips and techniques to help you reduce your tax burden, from leveraging deductions and credits to utilizing tax-deferred savings vehicles. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions and keep more of your hard-earned profits. Effective tax planning is crucial for success.
Maximizing Tax Savings for Small Business Owners
As a small business owner, navigating the complex world of taxes can be overwhelming. However, being tax savvy can help you save money and make informed decisions about your business. By understanding the tax laws and regulations, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your savings.
Understanding Tax Deductions for Small Business
One of the most effective ways to reduce your tax liability is by taking advantage of tax deductions. As a small business owner, you can deduct expenses related to your business, such as rent, utilities, and equipment purchases. It’s essential to keep accurate records of your expenses to ensure you’re taking advantage of all the deductions you’re eligible for.
| Common Tax Deductions for Small Business | Description |
|---|---|
| Home Office Deduction | A deduction for a portion of your rent or mortgage interest if you use a dedicated space for your business |
| Business Use of Your Car | A deduction for the business use percentage of your car expenses, including gas, maintenance, and insurance |
| Travel Expenses | A deduction for expenses related to business travel, including transportation, meals, and lodging |
Tax Credits for Small Business: What You Need to Know
Tax credits can provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax liability, making them a valuable tool for small business owners. Some common tax credits available to small businesses include the Work Opportunity Tax Credit and the Research and Development Tax Credit.
| Tax Credits for Small Business | Description |
|---|---|
| Work Opportunity Tax Credit | A credit for hiring individuals from targeted groups, such as veterans and low-income individuals |
| Research and Development Tax Credit | A credit for businesses that engage in research and development activities |
| Disabled Access Credit | A credit for businesses that make their facilities more accessible to individuals with disabilities |
Retirement Plan Contributions: A Tax-Advantaged Way to Save
As a small business owner, you can reduce your tax liability by making retirement plan contributions. By establishing a SEP-IRA or a solo 401(k), you can make tax-deductible contributions to your retirement account.
| Retirement Plan Contributions | Description |
|---|---|
| SEP-IRA | A retirement plan that allows you to make tax-deductible contributions for yourself and your employees |
| Solo 401(k) | A retirement plan designed for self-employed individuals and business owners with limited employees |
Tax Implications of Business Entity Structure
The business entity structure you choose can have significant tax implications. For example, a C corporation is taxed on its profits, and then shareholders are taxed again on dividends, resulting in double taxation.
| Business Entity Structure | Tax Implications |
|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | Business income is reported on the owner’s personal tax return |
| C Corporation | Double taxation: the corporation is taxed on profits, and shareholders are taxed on dividends |
| S Corporation | Pass-through taxation: income is passed through to shareholders and reported on their personal tax returns |
Staying Compliant with Tax Laws and Regulations
As a small business owner, it’s essential to stay compliant with tax laws and regulations to avoid penalties and fines. This includes filing tax returns on time, paying taxes owed, and maintaining accurate records.
| Tax Compliance | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax Return Filing | Filing tax returns on time to avoid penalties and fines |
| Tax Payment | Paying taxes owed to avoid interest and penalties |
| Record Keeping | Maintaining accurate and detailed records of business expenses and income |
How to reduce taxes on a small business?

To reduce taxes on a small business, it is essential to understand the various tax deductions and credits available. Tax planning is crucial to minimize tax liabilities and maximize savings. Small businesses can take advantage of various tax incentives, such as deductions for business expenses, depreciation, and retirement plans.
Maximizing Business Expense Deductions
Maximizing business expense deductions is a key strategy for reducing taxes on a small business. This involves identifying and documenting all eligible business expenses, including operating expenses, travel expenses, and equipment purchases. To maximize deductions, small businesses should:
- Maintain accurate and detailed records of all business expenses, including receipts and invoices.
- Take advantage of deductions for home office expenses, if applicable.
- Consider hiring a tax professional to ensure all eligible deductions are claimed.
Utilizing Tax Credits and Incentives
Utilizing tax credits and incentives is another effective way to reduce taxes on a small business. Tax credits can provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in tax liability, making them particularly valuable. Small businesses should explore available tax credits, such as:
- The Research and Development (R&D) tax credit, which can be claimed for qualified research expenses.
- The Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC), which can be claimed for hiring employees from targeted groups.
- The Disabled Access Credit, which can be claimed for expenses related to making a business more accessible to people with disabilities.
Implementing Tax-Deferred Retirement Plans
Implementing tax-deferred retirement plans is a strategic way to reduce taxes on a small business while also providing benefits to employees. Tax-deferred retirement plans, such as SEP-IRAs and 401(k) plans, allow businesses to make tax-deductible contributions, reducing taxable income. To implement a tax-deferred retirement plan effectively, small businesses should:
- Choose a plan that aligns with their business goals and employee needs.
- Consider the administrative costs and compliance requirements associated with the plan.
- Communicate the benefits of the plan to employees to encourage participation.
How much should I save for taxes as a small business owner?
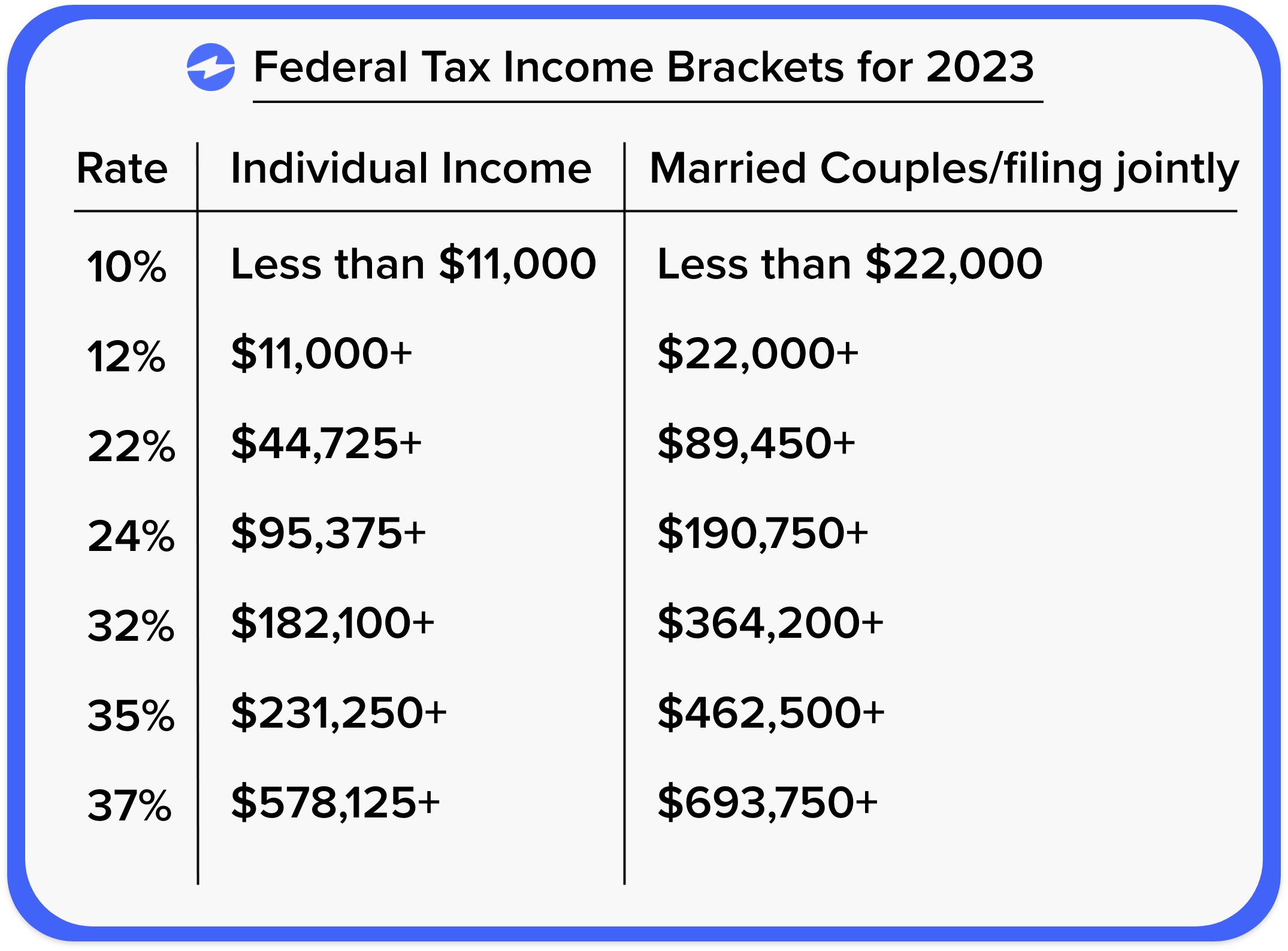
As a small business owner, it’s crucial to understand that tax savings are essential to maintaining a healthy cash flow and avoiding potential penalties. The amount you should save for taxes depends on several factors, including your business structure, income level, and the tax laws in your jurisdiction. Generally, it’s recommended to set aside a percentage of your monthly or quarterly earnings to cover your tax liability.
Understanding Your Business Tax Obligations
To determine how much you should save for taxes, you need to understand your business tax obligations. This includes knowing the tax rates applicable to your business, the frequency of tax payments, and any available tax deductions or credits.
- Identify your business tax rate based on your business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, S corporation, or C corporation).
- Familiarize yourself with tax filing frequencies (monthly, quarterly, or annually) and plan accordingly.
- Keep track of tax-deductible expenses to minimize your tax liability.
Calculating Your Tax Savings
Calculating the right amount for tax savings involves considering your business income, expenses, and tax obligations. You can use a tax calculator or consult with a tax professional to determine the optimal savings rate.
- Estimate your annual business income and project your tax liability.
- Consider self-employment taxes if you’re a sole proprietor or partner.
- Adjust your tax savings rate based on changes in your business income or expenses.
Best Practices for Tax Savings
To ensure you’re saving enough for taxes, implement best practices that help you stay on top of your tax obligations. This includes setting aside funds regularly, monitoring your tax liability, and adjusting your savings rate as needed.
- Set up a separate tax savings account to keep your tax funds separate from your operating funds.
- Regularly review your tax liability to ensure you’re on track with your savings.
- Consult with a tax professional to optimize your tax strategy and ensure compliance.
What are the three basic tax planning strategies?
The three basic tax planning strategies are fundamental concepts that individuals and businesses can utilize to minimize their tax liability. These strategies are crucial in ensuring that taxpayers can retain more of their income and make informed decisions about their financial affairs.
Tax Deferral Strategies
Tax deferral involves postponing tax payments to a later date, typically by delaying the recognition of income or accelerating deductions. This strategy can be beneficial as it allows taxpayers to retain the use of their money for a longer period. The key elements of tax deferral strategies include:
- Retirement Plans: Utilizing retirement plans such as 401(k) or IRA accounts to defer income until retirement.
- Depreciation: Accelerating depreciation on assets to reduce taxable income in the current period.
- Installment Sales: Reporting gains from sales over multiple periods to defer tax liability.
Income Shifting Strategies
Income shifting involves transferring income from one taxpayer to another, typically from a high-tax individual to a lower-tax individual. This can be achieved through various means, including gifting or establishing trusts. The key aspects of income shifting strategies include:
- Family Income Shifting: Transferring income to family members in lower tax brackets.
- Trusts: Establishing trusts to manage and distribute income to beneficiaries.
- Gifting: Gifting assets to individuals or charities to reduce taxable income.
Tax Avoidance through Exemptions and Credits
Tax avoidance through exemptions and credits involves utilizing specific provisions in the tax law to reduce or eliminate tax liability. Taxpayers can claim exemptions and credits for various activities, such as charitable donations or investments in certain industries. The key components of this strategy include:
- Charitable Donations: Claiming deductions for donations to qualified charitable organizations.
- Tax Credits: Claiming credits for specific activities, such as education expenses or investments in renewable energy.
- Exemptions: Claiming exemptions for certain types of income, such as municipal bond interest.
How can I be smart with taxes?

To be smart with taxes, it’s essential to understand the various strategies and techniques that can help minimize your tax liability. Being tax-smart involves more than just filing your tax return on time; it requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account your financial situation, investment decisions, and long-term goals. One key aspect is to stay informed about tax laws and regulations, which can change frequently.
Understanding Tax Deductions and Credits
Understanding tax deductions and credits is crucial for reducing your taxable income. Tax deductions and credits can significantly lower your tax bill, but they require careful planning and documentation. To maximize your tax savings, you should be aware of the various deductions and credits available, such as those for charitable donations, mortgage interest, and education expenses.
- Keep accurate records of your expenses to support your claims for deductions and credits, including receipts and bank statements.
- Consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re taking advantage of all the deductions and credits you’re eligible for, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC).
- Consider bunching deductions, where you group multiple years’ worth of expenses into a single year to exceed the standard deduction threshold.
Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
Implementing tax-efficient investment strategies can help minimize the tax impact on your investments. This involves considering the tax implications of your investment decisions and choosing investments that are tax-friendly. For example, tax-loss harvesting involves selling securities that have declined in value to offset gains from other investments, thereby reducing your tax liability.
- Invest in tax-deferred accounts, such as 401(k) or IRA, to delay paying taxes on your investment earnings until withdrawal.
- Consider holding tax-efficient investments, such as index funds or municipal bonds, which tend to generate fewer taxable distributions.
- Be mindful of the wash sale rule, which prohibits claiming a loss on a security if you purchase a substantially identical security within 30 days.
Planning for Tax Implications in Financial Decisions
Planning for the tax implications of your financial decisions is vital to being smart with taxes. This includes considering the tax consequences of major financial decisions, such as selling a business or inheriting assets. Understanding how these events will impact your tax situation can help you make more informed decisions and potentially reduce your tax liability.
- Consider the tax implications of selling a primary residence, which may be exempt from capital gains tax under certain conditions.
- Understand the tax rules surrounding inherited assets, including the potential for a stepped-up basis, which can reduce capital gains tax.
- Plan for the tax implications of retirement account distributions, which can impact your tax bracket and overall tax liability in retirement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective tax-saving strategies for small businesses?
Small businesses can implement various tax-saving strategies to minimize their tax liability. One effective approach is to take advantage of tax deductions and credits. This can include deductions for business expenses, such as equipment, supplies, and travel expenses, as well as credits for research and development, hiring certain employees, and investing in renewable energy. Additionally, small businesses can consider retirement plans, such as SEP-IRAs or solo 401(k)s, which can provide significant tax benefits. By understanding and utilizing these strategies, small businesses can reduce their tax burden and improve their bottom line.
How can small businesses maximize their tax deductions?
To maximize tax deductions, small businesses should maintain accurate and detailed records of their business expenses. This includes keeping receipts, invoices, and bank statements, as well as categorizing expenses correctly. Small businesses can also consider accelerating deductions by paying expenses early or bunching them together. Furthermore, they can take advantage of special deductions, such as the Section 179 deduction for equipment purchases or the home office deduction for businesses operated from home. By being proactive and organized, small businesses can ensure they are taking advantage of all the deductions available to them.
What are the tax implications of different business structures?
The business structure chosen by a small business can have significant tax implications. For example, sole proprietorships and single-member LLCs are typically pass-through entities, meaning that business income is only taxed at the individual level. In contrast, C-corporations are subject to double taxation, where the corporation is taxed on its profits and shareholders are taxed on dividends received. S-corporations and partnerships are also pass-through entities, but have different rules and restrictions. By understanding the tax implications of different business structures, small businesses can make informed decisions about their organizational structure.
How can small businesses stay up-to-date with changing tax laws and regulations?
Staying up-to-date with changing tax laws and regulations is crucial for small businesses to ensure compliance and minimize their tax liability. One way to do this is to work with a qualified tax professional, who can provide guidance on tax planning and preparation. Small businesses can also stay informed through tax industry publications and government websites, such as the IRS website. Additionally, they can participate in tax seminars and webinars, which can provide updates on tax law changes and best practices for tax planning. By staying informed, small businesses can adapt to changes in the tax landscape and make informed decisions about their tax strategy.