Understanding employment law is crucial for human resource professionals to navigate the complex landscape of workplace regulations. As the backbone of organizational compliance, HR practitioners must stay informed about key rules governing employment practices. This article outlines essential employment law principles that HR professionals need to know, covering critical areas such as hiring, employee rights, and termination procedures. By grasping these must-know rules, HR teams can minimize risks, ensure fair treatment, and foster a positive work environment, ultimately protecting both employees and the organization. Effective HR practice relies on a deep understanding of these regulations.
Understanding the Foundations of Employment Law
Employment law is a crucial aspect of human resource practice that governs the relationship between employers and employees. It encompasses a wide range of regulations and statutes that dictate how employers should treat their employees, the rights of employees, and the obligations of employers. Understanding the foundations of employment law is essential for HR professionals to ensure compliance and maintain a fair and respectful workplace.
The Importance of Employment Contracts
Employment contracts are a fundamental component of employment law, outlining the terms and conditions of employment. These contracts can be written or implied and cover aspects such as job responsibilities, compensation, and termination procedures. A well-drafted employment contract can protect both the employer and the employee by clearly defining their respective rights and obligations.
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Responsibilities | Clearly outlines the duties and expectations of the employee’s role. |
| Compensation and Benefits | Details the salary, bonuses, and benefits the employee is entitled to. |
| Termination Procedures | Specifies the conditions under which the contract can be terminated by either party. |
Anti-Discrimination Laws in the Workplace
Anti-discrimination laws are a critical aspect of employment law, ensuring that employees are not discriminated against based on certain characteristics such as race, gender, age, or disability. Employers must adhere to these laws in all aspects of employment, including hiring, promotion, and termination.
| Protected Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|
| Race and Color | Prohibits discrimination based on an individual’s racial or ethnic background. |
| Gender and Sexual Orientation | Protects against discrimination based on gender identity or sexual orientation. |
| Age | Prohibits age-based discrimination against employees aged 40 or older. |
Workplace Safety and Health Regulations
Workplace safety and health regulations are designed to ensure a safe working environment for employees. Employers are required to comply with these regulations, which include providing a hazard-free workplace, training employees on safety procedures, and maintaining records of workplace injuries.
| Regulatory Requirements | Description |
|---|---|
| Hazard Communication | Requires employers to inform employees about potential workplace hazards. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Mandates the use of PPE to minimize exposure to hazards. |
| Injury and Illness Reporting | Employers must record and report workplace injuries and illnesses. |
Employee Leave and Benefits
Employment law also governs employee leave and benefits, including provisions for family and medical leave, vacation time, and health insurance. Employers must comply with these regulations to ensure that employees receive the benefits they are entitled to.
| Leave and Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) | Provides eligible employees with unpaid leave for certain family and medical reasons. |
| Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) | Protects the privacy and security of employee health information. |
| COBRA Benefits | Allows employees to continue health coverage after leaving employment. |
Termination of Employment
The termination of employment is a significant aspect of employment law, governed by regulations that protect employees from unfair dismissal. Employers must have a valid reason for terminating an employee and follow the correct procedures to avoid potential claims of unfair dismissal.
| Termination Procedures | Description |
|---|---|
| Notice Period | Requires employers to provide employees with adequate notice before termination. |
| Severance Pay | May be required or negotiated as part of the termination agreement. |
| Final Paycheck | Employers must provide employees with their final paycheck, including accrued wages and benefits. |
What are the three most important HR laws?
The three most important HR laws are regulations that govern the relationship between employers and employees, protecting the rights of workers and outlining the responsibilities of employers. These laws are crucial for maintaining a fair and safe work environment.
Employment Discrimination Laws
Employment discrimination laws are essential for ensuring that all employees are treated fairly and without bias. These laws prohibit employers from discriminating against employees or job applicants based on certain characteristics. The key aspects of employment discrimination laws include:
- Protected Characteristics: Laws protect against discrimination based on characteristics such as age, sex, race, disability, and religion.
- Equal Employment Opportunities: Employers must provide equal opportunities for hiring, promotion, and compensation.
- Retaliation Protection: Employees are protected from retaliation when they report discrimination or participate in investigations.
Wage and Hour Laws
Wage and hour laws regulate the payment of wages and the number of hours employees can work. These laws are designed to ensure that employees are fairly compensated for their work. The main components of wage and hour laws include:
- Minimum Wage Requirements: Employers must pay employees at least the minimum wage set by law.
- Overtime Pay: Employees are entitled to overtime pay for work exceeding a certain number of hours in a week.
- Record Keeping: Employers must maintain accurate records of hours worked and wages paid.
Workplace Safety and Health Laws
Workplace safety and health laws are designed to protect employees from hazards in the workplace. These laws require employers to provide a safe working environment and to comply with health and safety regulations. The critical elements of workplace safety and health laws include:
- Hazard Reporting: Employees have the right to report hazards without fear of retaliation.
- Safety Training: Employers must provide training to employees on workplace hazards and safety procedures.
- Compliance with Regulations: Employers must comply with specific regulations and standards to ensure workplace safety.
What are the HR rules and regulations?
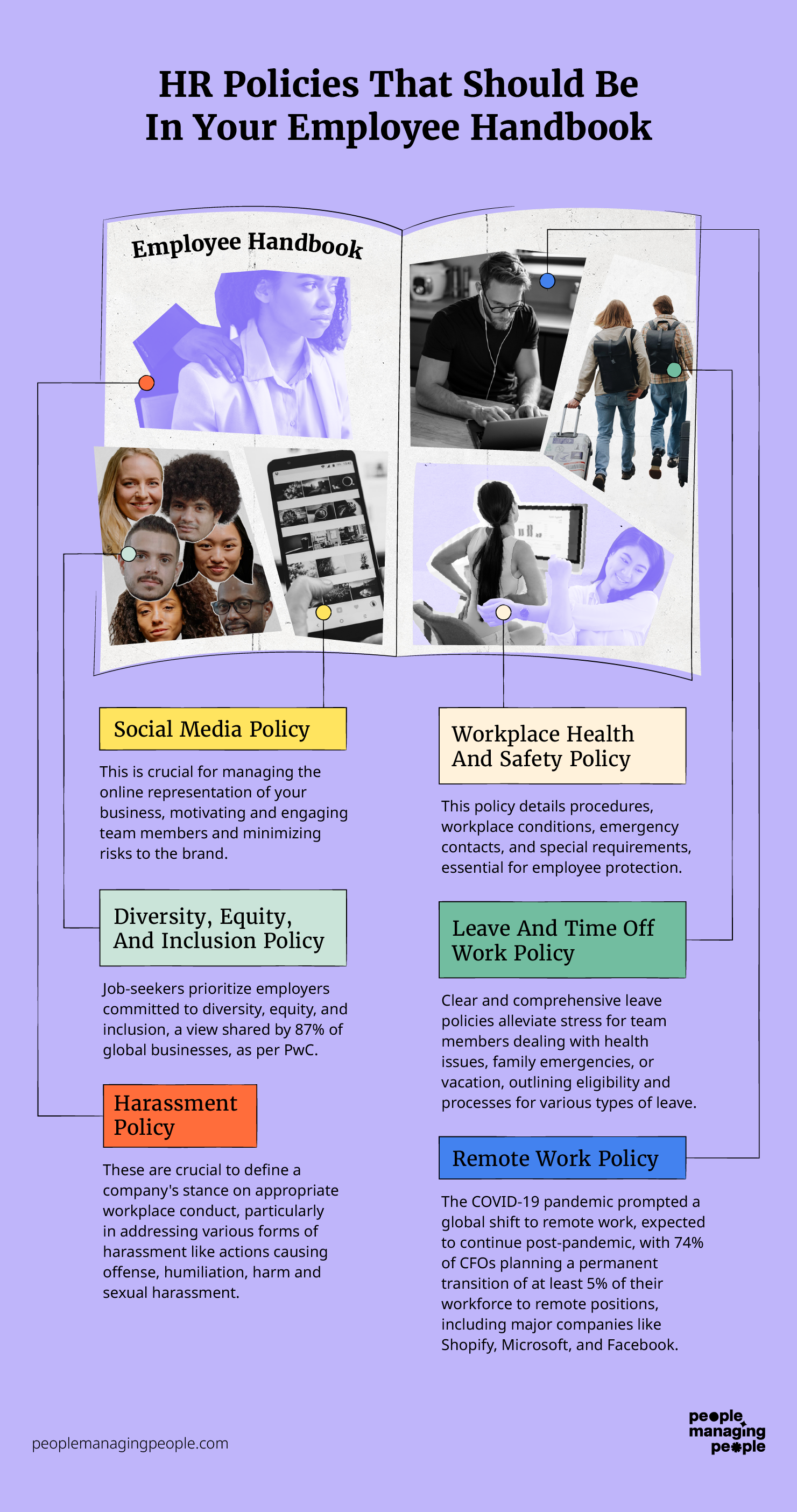
HR rules and regulations are the guidelines that govern the management of employees within an organization. These rules are designed to ensure compliance with labor laws, promote a positive work environment, and protect the rights of both employees and employers. The specific HR rules and regulations can vary depending on the country, industry, and company size.
Key Components of HR Rules and Regulations
The key components of HR rules and regulations include policies related to employee conduct, equal employment opportunities, and workplace safety. These policies are crucial for maintaining a fair and respectful work environment. Here are some key aspects:
- Employee Conduct: Rules governing behavior such as attendance, dress code, and use of company resources.
- Equal Employment Opportunities: Policies ensuring non-discrimination based on race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics.
- Workplace Safety: Regulations aimed at preventing workplace injuries and illnesses.
Compliance with Labor Laws
Compliance with labor laws is a critical aspect of HR rules and regulations. This includes adherence to laws governing minimum wage, overtime pay, and employee benefits. Organizations must stay updated on changes to labor laws to avoid legal repercussions. Key compliance areas include:
- Minimum Wage and Overtime: Ensuring that employees are paid fairly for their work, including overtime compensation.
- Employee Benefits: Providing benefits as required by law, such as health insurance or retirement plans.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of employee data, payroll, and other HR-related information.
Importance of Effective HR Policies
Effective HR policies are essential for fostering a positive and productive work environment. They help in reducing legal risks, improving employee morale, and enhancing organizational performance. Well-crafted HR policies can also contribute to attracting and retaining top talent. The benefits include:
- Reducing Legal Risks: Minimizing the risk of lawsuits and legal penalties through compliance with labor laws.
- Improving Employee Morale: Creating a fair and respectful workplace that boosts employee satisfaction and engagement.
- Enhancing Organizational Performance: Aligning HR practices with business objectives to drive organizational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key employment laws that HR professionals must be aware of to ensure compliance?
HR professionals must be knowledgeable about various employment laws to ensure their organization’s compliance and avoid potential lawsuits. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Additionally, The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations to individuals with disabilities. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) regulates minimum wage, overtime, and child labor provisions. Understanding these laws and their implications is crucial for HR professionals to develop and implement compliant policies and practices.
How can employers ensure they are complying with anti-discrimination laws in the hiring process?
To comply with anti-discrimination laws, employers should focus on creating a fair and unbiased hiring process. This involves avoiding discriminatory language in job postings and ensuring that the criteria used to select candidates are job-related and consistent with business needs. Employers should also train hiring managers and interviewers on recognizing and avoiding bias. Furthermore, maintaining detailed records of the hiring process can help employers demonstrate their compliance with anti-discrimination laws if faced with a discrimination claim.
What are the essential components of an employee handbook that complies with employment laws?
An employee handbook that complies with employment laws should clearly outline the company’s policies and procedures. It should include anti-discrimination and anti-harassment policies, as well as procedures for reporting and addressing complaints. The handbook should also cover employee classification, compensation, and benefits, ensuring compliance with laws like the FLSA. Additionally, it should provide information on employee rights under the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) and other relevant laws. Regularly reviewing and updating the handbook is essential to reflect changes in employment laws and company policies.
Can employers require employees to sign arbitration agreements as a condition of employment?
Employers may require employees to sign arbitration agreements as a condition of employment, but the enforceability of such agreements depends on various factors. The Federal Arbitration Act (FAA) generally supports the enforceability of arbitration agreements, but courts may scrutinize agreements that are deemed unconscionable or overly broad. Employers must ensure that their arbitration agreements are clearly drafted and provide employees with a fair process for resolving disputes. Employers should also be aware that certain laws, such as those related to sexual harassment claims, may limit the enforceability of arbitration agreements.