When filing a claim for short-term disability benefits, many individuals expect a straightforward process, but unfortunately, denials are common. Understanding the reasons behind these denials is crucial for those seeking financial support during a period of incapacity. Various factors can lead to a denial, ranging from insufficient medical evidence to pre-existing condition exclusions. Being aware of these potential pitfalls can help applicants prepare and potentially avoid a denial, ensuring they receive the benefits they are entitled to during a challenging time.
Understanding the Reasons Behind Short-Term Disability Denial
Short-term disability benefits are designed to provide financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to a medical condition or injury. However, not all claims are approved, and understanding the reasons behind a denial is crucial for a successful appeal. The denial of short-term disability benefits can be a complex issue, influenced by various factors related to the claim, the policy, and the claimant’s condition.
Insufficient Medical Evidence
One of the primary reasons short-term disability claims are denied is the lack of sufficient medical evidence to support the claim. Insurance companies require detailed medical documentation to verify the claimant’s condition and its impact on their ability to work. This includes medical records, test results, and statements from healthcare providers.
| Required Documents | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical Records | Detailed records of the claimant’s medical history and current condition. |
| Test Results | Results of relevant medical tests that support the claim. |
| Healthcare Provider Statements | Statements or reports from healthcare providers explaining the claimant’s condition and its impact on their ability to work. |
Pre-Existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions can be a reason for denial if the insurance company determines that the condition was not disclosed or was misrepresented on the insurance application. It’s essential to understand how pre-existing conditions are handled under the policy.
| Pre-Existing Condition Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Disclosure Requirement | The condition must have been disclosed on the insurance application. |
| Condition Stability | The condition’s stability and treatment history before the policy’s effective date. |
| Policy Terms | The specific terms of the policy regarding pre-existing conditions. |
Failure to Meet the Policy’s Definition of Disability
Each insurance policy has its own definition of disability, and claimants must meet this definition to qualify for benefits. The definition often involves the inability to perform the duties of one’s own occupation or any occupation for which they are suited based on education, training, or experience.
| Disability Definition Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Own Occupation | The inability to perform the duties of one’s current occupation. |
| Any Occupation | The inability to perform the duties of any occupation for which the claimant is suited. |
| Material Duties | The inability to perform the material duties of their occupation. |
Not Under Appropriate Care
Insurance companies often require claimants to be under the appropriate care of a healthcare provider. This means receiving treatment that is consistent with the condition and its severity.
| Appropriate Care Requirements | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Treatment | Regular visits or consultations with a healthcare provider. |
| Treatment Consistency | The treatment received must be consistent with the condition. |
| Healthcare Provider Qualifications | The healthcare provider’s qualifications and expertise in treating the condition. |
Failure to Comply with Treatment Plans
Claimants are expected to comply with their treatment plans as prescribed by their healthcare providers. Failure to do so can be grounds for denial if the insurance company believes that compliance would improve the claimant’s condition or enable them to return to work.
| Compliance Expectations | Description |
|---|---|
| Adherence to Medication | Taking prescribed medication as directed. |
| Attendance at Therapy Sessions | Attending scheduled physical therapy or other treatment sessions. |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Making necessary lifestyle adjustments as recommended by healthcare providers. |
Why is it so hard to get short-term disability?
It is challenging to obtain short-term disability benefits due to several factors. Insurance companies often have strict eligibility criteria, and the application process can be complex and time-consuming. The primary reason is that disability insurance is designed to provide financial support to individuals who are genuinely unable to work due to a medical condition, and insurers must carefully assess each claim to ensure it meets the policy’s requirements.
Stringent Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for short-term disability benefits are often stringent, making it difficult for individuals to qualify. To be eligible, applicants must typically provide medical documentation that supports their claim, demonstrating that their condition prevents them from performing their job duties. The documentation must come from a qualified healthcare professional and meet specific requirements set by the insurer.
- The applicant must have a medically diagnosed condition that is covered under the policy.
- The condition must be so severe that it prevents the individual from performing their occupational duties.
- The applicant must have been under regular medical treatment for the condition.
Lack of Understanding of Disability Policies
Many individuals struggle to navigate the complexities of disability insurance policies, leading to confusion and frustration. The policies often contain specific clauses and exclusions that can be difficult to understand, and applicants may not be aware of the requirements for filing a successful claim.
- Applicants may not fully comprehend the definition of disability as outlined in the policy.
- The pre-approval process and the requirements for ongoing treatment may be unclear.
- There may be exclusions or limitations in the policy that affect the applicant’s eligibility.
Insufficient Medical Evidence
Insufficient medical evidence is a common reason for disability claim denials. Insurers require robust medical documentation to support a claim, and if the provided evidence is incomplete or inadequate, the claim may be rejected.
- The medical documentation may not be comprehensive or up-to-date.
- The healthcare provider’s notes and records may not adequately support the claimed disability.
- The insurer may require additional medical assessments or evaluations to validate the claim.
What are the odds of getting a short-term disability?
The odds of getting a short-term disability depend on various factors, including the type of disability, the individual’s occupation, and the specific insurance policy. Generally, short-term disability insurance provides partial income replacement for a limited period, usually up to 90 days, when an individual is unable to work due to illness, injury, or pregnancy.
Factors Affecting Short-Term Disability Odds
The likelihood of getting a short-term disability is influenced by several factors. The most significant factors include the individual’s health condition, occupation, and insurance policy terms. For instance, individuals working in high-risk occupations, such as construction or healthcare, may be more likely to file a short-term disability claim. The following factors can affect the odds:
- Pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can increase the likelihood of filing a claim.
- Occupational hazards, such as exposure to chemicals or physical strain, can also contribute to a higher risk of disability.
- Age and lifestyle factors, such as smoking or lack of exercise, can also impact an individual’s likelihood of becoming disabled.
Common Causes of Short-Term Disability
Short-term disabilities can result from a range of causes, including acute illnesses, injuries, and pregnancy-related complications. The most common causes of short-term disability vary depending on the individual’s age, occupation, and health status. Some common causes include:
- Musculoskeletal disorders, such as back pain or tendonitis, which can be caused by repetitive strain or physical trauma.
- Mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety, which can be triggered by stress or trauma.
- Pregnancy and childbirth, which can be a common cause of short-term disability for women, particularly those with complications during pregnancy or delivery.
Insurance Policy Considerations
The terms and conditions of an individual’s insurance policy can significantly impact their likelihood of receiving short-term disability benefits. Policyholders should carefully review their policy to understand the eligibility criteria, benefit amounts, and exclusions. Key considerations include:
- Elimination periods, which can range from 0 to 180 days, during which the individual must be disabled before receiving benefits.
- Benefit periods, which can vary from a few weeks to several months, determining how long the individual can receive benefits.
- Pre-existing condition clauses, which may exclude or limit coverage for certain conditions, depending on the policy terms.
Why do most people get denied for disability?

Most people get denied for disability due to various reasons related to the complexity and strictness of the disability claims process. The Social Security Administration (SSA) has a rigorous evaluation process to determine whether an individual is eligible for disability benefits. The SSA assesses the severity of the individual’s condition, their ability to perform substantial gainful activity (SGA), and whether their condition is listed in the SSA’s Blue Book, which contains a list of disabling conditions.
Medical Documentation and Evidence
One of the primary reasons people get denied for disability is due to inadequate medical documentation. The SSA requires thorough medical evidence to support a disability claim, including detailed medical records, test results, and statements from healthcare providers.
- The claimant’s medical records may not be up-to-date or comprehensive enough to support their claim.
- The SSA may not have received sufficient information from the claimant’s healthcare providers to assess the severity of their condition.
- The medical evidence may not be consistent with the claimant’s allegations of disability.
Ability to Perform Substantial Gainful Activity
The SSA evaluates whether the claimant is capable of performing substantial gainful activity (SGA), which is work that earns a certain amount of money per month. If the SSA determines that the claimant can perform SGA, their claim will likely be denied.
- The SSA assesses the claimant’s residual functional capacity (RFC) to determine what they can still do despite their medical condition.
- The claimant’s age, education, and work experience are also considered when determining their ability to perform SGA.
- The SSA may use the services of a vocational expert to determine whether the claimant can perform other jobs in the national economy.
Blue Book Listings and Technical Denials
The SSA maintains a list of disabling conditions in the Blue Book, and if a claimant’s condition is not listed, their claim may be denied. Additionally, technical denials can occur due to issues such as insufficient work credits or exceeding income limits.
- The claimant’s condition may not meet the specific criteria listed in the Blue Book.
- The SSA may deny the claim due to technical reasons, such as the claimant not having worked long enough to earn sufficient work credits.
- The claimant’s income or resources may exceed the SSA’s limits for disability eligibility.
Does back pain qualify for short-term disability?

Back pain can be a debilitating condition that affects an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and job-related activities. The eligibility for short-term disability benefits due to back pain depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the type of job the individual performs, and the specific requirements of the disability insurance policy.
Understanding Short-Term Disability Benefits
Short-term disability benefits are designed to provide financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to a medical condition. To qualify for these benefits, the individual must have a condition that meets the definition of disability under their insurance policy. In the case of back pain, the condition must be severe enough to prevent the individual from performing their job duties.
- The insurance policy will typically require medical documentation to support the claim, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and any relevant test results.
- The individual’s healthcare provider must provide detailed information about the condition, including its impact on the individual’s ability to work.
- The insurance company will review this information to determine whether the individual meets the policy’s definition of disability.
Factors Affecting Eligibility for Short-Term Disability Due to Back Pain
The eligibility for short-term disability benefits due to back pain is influenced by several factors. The severity of the back pain and its impact on the individual’s ability to perform job-related tasks are crucial. Additionally, the type of job the individual has and the specific requirements of their disability insurance policy play significant roles.
- The severity of the back pain and its impact on daily activities and job duties are critical factors.
- The individual’s job requirements, including physical demands such as lifting, bending, or standing for long periods.
- The specific terms and conditions of the disability insurance policy, including the definition of disability and any exclusions or limitations.
Documentation and Evidence Required for a Successful Claim
To successfully claim short-term disability benefits due to back pain, it is essential to provide comprehensive medical documentation and evidence. This includes detailed medical records, diagnoses, treatment plans, and any relevant test results.
- Comprehensive medical records that detail the diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of the back pain.
- Documentation from healthcare providers that explains how the back pain affects the individual’s ability to perform their job duties.
- Any additional evidence that supports the claim, such as imaging studies or reports from physical therapists.
Can your employer deny your disability benefits?

The answer to this question largely depends on the specific circumstances and the laws governing disability benefits in your jurisdiction. Generally, an employer can deny disability benefits if the employee does not meet the eligibility criteria as outlined in the company’s disability benefits policy or the applicable laws. For instance, if an employee’s condition does not qualify as a disability under the policy, the employer may deny the benefits.
Understanding Disability Benefits Eligibility
To determine whether an employer can deny disability benefits, it’s crucial to understand the eligibility criteria. Typically, disability benefits are available to employees who are unable to work due to a medical condition or disability. The specific requirements may vary depending on the employer’s policy or the relevant laws, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States. Key factors that influence eligibility include:
- The nature and severity of the employee’s medical condition or disability.
- The employee’s ability to perform their job duties or any other job duties within the company.
- The duration of the employee’s disability, as some policies require a minimum period of disability before benefits become available.
Reasons for Denial of Disability Benefits
Employers or insurance companies may deny disability benefits for several reasons. A common reason is that the employee’s condition does not meet the definition of disability under the policy or applicable law. Other reasons may include:
- Insufficient medical evidence to support the claim, such as a lack of detailed medical records or opinions from qualified healthcare professionals.
- The employee’s condition is considered a pre-existing condition that is not covered under the policy.
- The employer or insurance company disputes the extent to which the disability prevents the employee from working.
Appealing a Denial of Disability Benefits
If an employer denies disability benefits, the employee typically has the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process may involve submitting additional medical evidence, requesting a review by an independent third party, or filing a complaint with a relevant government agency. Key steps in the appeals process include:
- Reviewing the denial letter to understand the reasons for the denial and the specific steps required to appeal.
- Gathering and submitting additional medical evidence or other supporting documentation.
- Filing a formal appeal with the employer or insurance company, or seeking assistance from a government agency or legal professional.
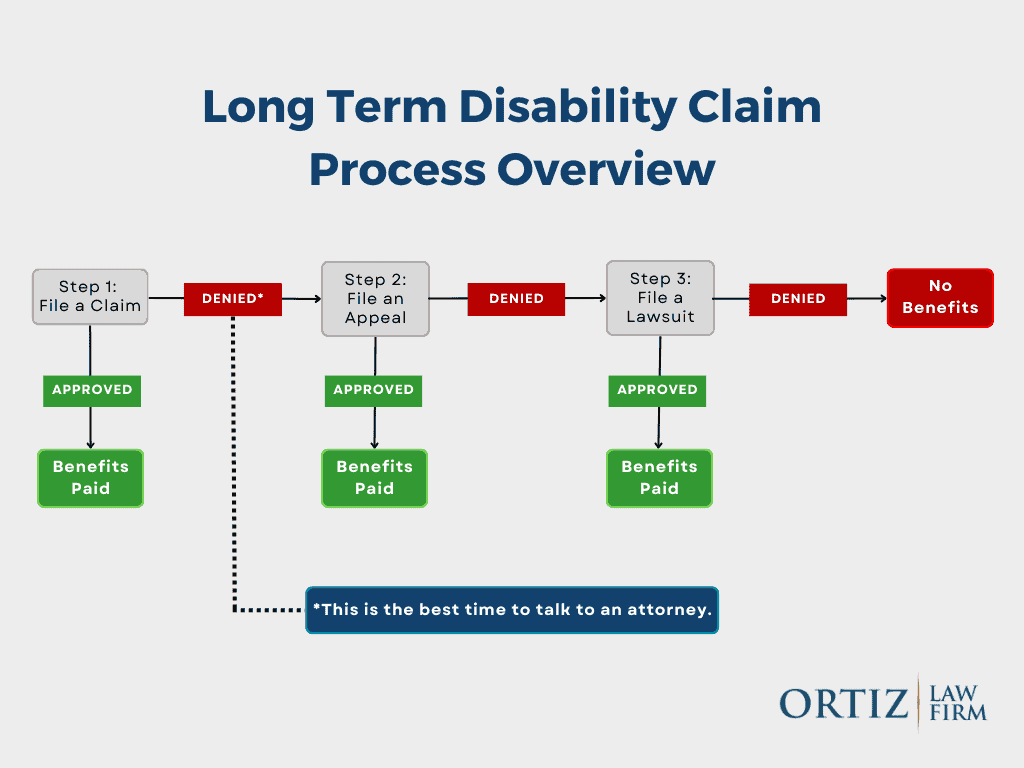
Can short-term disability be denied for pre-existing conditions?
Generally, insurance companies can deny short-term disability benefits if the condition that is being claimed is considered a pre-existing condition. The definition of a pre-existing condition varies among insurance providers, but it typically refers to a condition for which the claimant received medical treatment or advice within a certain period before the policy’s effective date. Insurance companies often have specific clauses that exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions for a certain period.
Understanding Pre-Existing Conditions Clauses
Insurance policies often contain clauses that specifically address how pre-existing conditions are handled. These clauses can vary significantly from one insurance provider to another. Understanding these clauses is crucial for determining whether a claim might be denied. The specifics of these clauses can include the definition of a pre-existing condition, the time frame considered for determining pre-existing conditions, and any exceptions that might be made.
- The definition of a pre-existing condition is typically outlined in the policy, including what constitutes medical treatment or advice.
- The look-back period is another critical aspect, as it specifies how far back the insurer will review medical history to determine if a condition is pre-existing.
- Some policies may offer a waiver of pre-existing condition exclusion after a certain period of continuous coverage.
Factors Influencing Denial for Pre-Existing Conditions
Several factors can influence whether a claim for short-term disability benefits will be denied due to a pre-existing condition. These include the specifics of the insurance policy, the nature of the condition being claimed, and the claimant’s medical history. Insurance companies assess these factors to determine whether the condition was indeed pre-existing and if it falls under the exclusions outlined in the policy.
- The specific terms of the insurance policy are crucial, as they define what is covered and what is not, including how pre-existing conditions are treated.
- The claimant’s medical history is reviewed to assess if there was any treatment or diagnosis related to the condition before the policy’s effective date.
- The insurer’s definition and application of the pre-existing condition clause can significantly affect the outcome of a claim.
Appealing a Denial for Pre-Existing Conditions
If a claim for short-term disability benefits is denied due to a pre-existing condition, the claimant has the right to appeal. The appeals process typically involves providing additional medical evidence or challenging the insurer’s interpretation of the pre-existing condition clause. It is essential to understand the appeals process and to gather all necessary documentation to support the appeal.
- Gathering additional medical evidence that may not have been considered during the initial review can be crucial for a successful appeal.
- Reviewing the insurer’s decision to ensure it aligns with the policy’s terms and to identify any potential misinterpretation of the pre-existing condition clause.
- Seeking professional assistance, such as from an attorney specializing in insurance law, can be beneficial in navigating the appeals process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common reasons for short-term disability denial?
Short-term disability claims can be denied due to several reasons. Insufficient medical evidence is a common reason, where the insurance company feels that the provided medical documentation does not adequately support the claim. Additionally, if the condition is not severe enough to prevent the individual from performing their job duties, the claim may be denied. Other reasons include pre-existing conditions not being properly disclosed or covered under the policy, and failure to follow the treatment plan recommended by the healthcare provider. It’s crucial to understand the policy’s terms and conditions to avoid denial.
Can a short-term disability claim be denied due to a pre-existing condition?
Yes, a short-term disability claim can be denied if the insurance company determines that the condition is pre-existing and was not disclosed or covered under the policy. Insurance companies often have a look-back period during which they review the applicant’s medical history to identify pre-existing conditions. If a condition is deemed pre-existing and the policy does not cover it, the claim will likely be denied. It’s essential to review the policy’s terms regarding pre-existing conditions before filing a claim.
How does failure to provide adequate medical documentation affect short-term disability claims?
Failure to provide adequate medical documentation is a significant reason for short-term disability claim denials. Insurance companies require detailed medical records and sometimes additional information from healthcare providers to assess the validity of a claim. If the provided documentation is insufficient or does not clearly demonstrate the severity of the condition, the insurance company may deny the claim. Ensuring that all medical records are thorough and support the claim is vital.
What role does the definition of ‘disability’ play in short-term disability denials?
The definition of ‘disability’ as per the insurance policy plays a crucial role in determining whether a short-term disability claim is approved or denied. If the insurance company determines that the claimant’s condition does not meet the policy’s definition of disability, the claim will be denied. Policies often have specific criteria that must be met to qualify as disabled. Understanding the policy’s definition of disability and how it applies to the individual’s condition is key to a successful claim.